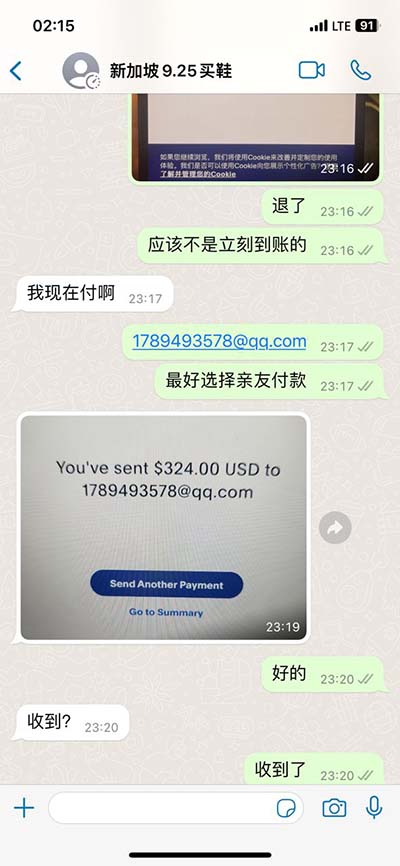
the fall of rolex The Rolex Lady-Datejust in steel and gold has a current average price of $3,892, up 2.6 percent from last year. Rolex’s gold Day-Date, from the 1970s and 80s, increased by 1.4 percent to.
Amazon.com, Inc. Common Stock (AMZN) Stock Price, Quote, News & History | Nasdaq. 1D. 5D. 1M. 6M. YTD. 1Y. 5Y. MAX. Key Data. Data Disclaimer: The Nasdaq Indices and the Major Indices.
0 · why are rolex prices going down
1 · why are rolex dealers panicking
2 · rolex stock buy or sell
3 · rolex resale news
4 · rolex prices going up
5 · rolex price trends
6 · rolex price predictions
7 · rolex price dropping
Colorway Dark Grey. Main Color Grey. Shop the Ami Oversized Scarf 'Dark Grey' and other curated styles from Ami on GOAT. Buyer protection guaranteed on all purchases.
nueva coleccion lentes gucci mujer
For a full year, pre-owned Rolex prices have been on a steady decline. Despite a few notable anomalies (which you’ll find below), right now is an excellent time to buy vintage, neo-vintage and . A new report from Morgan Stanley shows that Rolex prices are starting to fall fast on the secondary market. Here's what that means.
Prices for modern Rolex models on secondary channels skyrocketed over the past eight months. Now that they're softening, dealers say relax. Rolex prices rose by 0.33% in August, according to the Bloomberg Subdial Watch Index, which tracks the top 50 most traded watch references. Meanwhile, California-based . Rolex’s apparent caution on 2024 might be because its lead versus rivals has narrowed in a wider market that’s decelerating. The Rolex Lady-Datejust in steel and gold has a current average price of ,892, up 2.6 percent from last year. Rolex’s gold Day-Date, from the 1970s and 80s, increased by 1.4 percent to.
sandali prada outlet online
The Rolex Market Index, which tracks the 30 most valuable models, is down 8% from a year ago, while the Patek Philippe index lost 16%. Audemars Piguet saw the sharpest losses, down 19% year on . The fall of the Roman Empire in AD 476 marked a pivotal moment in history, leading to the end of an era that had seen the empire stretch from Britain to North Africa and from Spain to the Middle East. While the exact reasons for the fall are complex and multifaceted, historians have identified several key internal and external factors that contributed to this .Where one historian may suggest the fall occurred in 476 AD after years of internal corruption and barbarian invasion, another may advocate that Rome never actually fell until 1453. However, what cannot be contested are the . Richard A. Gabriel, a distinguished professor of history and war studies at the Royal Military College of Canada, is the author of more than 40 books. For further reading he recommends Empires and Barbarians: The Fall .
As British historian Bryan Ward-Perkins argues in The Fall of Rome and the End of Civilization, "The end of the Roman West witnessed horrors and dislocation that it is difficult to parallel." In many ways, Rome‘s fall was a victim of its own success. The Empire‘s sheer size and complexity made it increasingly difficult to govern effectively.Therefore, the "fall of Rome" really refers only to the fall of the western half of the Empire. Other fundamental problems contributed to the fall. In the economically ailing west, a decrease in agricultural production led to higher food prices. The western half of the empire had a large trade deficit with the eastern half.
This Fall of Rome timeline, however, uses standard events and marks the end with British historian Edward Gibbon's conventionally accepted date for the fall of Rome at 476 CE, as described in his famous history entitled The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire.So this timeline begins just before the east-west splitting of the Roman Empire, a time described as . Varro, a Republican Roman antiquarian, dated the founding of Rome to the 21st of April 753 B.C. While canonical, the date is most likely wrong. The fall of Rome also has a traditional date -- about a millennium later, on September 4, A.D. 476, a date established by the historian Edward Gibbon. Government corruption and political instability were also contributing factors to the empire’s eventual fall. A series of weak emperors from the second century had seen more than 20 men on the imperial throne in just 75 years, thanks in part to the Praetorian Guard – bodyguards to the emperor – which was using its power to decide to promote, or kill off, would . Decadence in some form is another popular single-issue cause of the fall. Edward Gibbon’s massive 1776 to 1789 work The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, was a proponent of this idea. Gibbon argued that Romans became effeminate and weak, unwilling to make the sacrifices necessary to defend their territories.
Rome was known as the Eternal City; however, the city's position as the center of a global empire was anything but eternal. There were three major causes for the fall of the empire: The cataclysmic end of the Roman Empire in the West has tended to mask the underlying features of continuity. The map of Europe in the year 500 would have been unrecognizable to anyone living a hundred years earlier. Gone was the solid boundary line dividing Roman civilization from what had been perceived as 'barbarism'. Gone were the .
Brilliant though it was, the thesis he expounded in his monumental and highly engaging magnum opus The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire—he argued that the rise of Christianity emasculated the native vigor of Rome, leaving it open to more virile conquerors, i.e. barbarians—is a proposition full of holes and inconsistencies, saying in the .
Another factor that contributed to the decline and fall of the Roman empire was that during the last 400 years of the empire, the scientific achievements of the Romans were limited almost entirely to engineering and the organization of public services. They built marvelous roads, . When the historian Ian Morris at Stanford University created a universal social-development index, the fall of Rome emerged as the greatest setback in the history of human civilization. Stanford historian Walter Scheidel calls the fall of Rome the “great escape.” (Image credit: Daniel Hinterramskogler) Romulus Augustus, the last emperor of the Western Roman Empire, is deposed by Odoacer, a German barbarian who proclaims himself king of Italy. This augurs what many historians consider the fall of .
Why a Rolex watch is No Longer Unique. The Saturation of Popular Models 🤷♂️#Rolex #RolexCollector #RolexWatch #WatchThe History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, sometimes shortened to Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, is a six-volume work by the English historian Edward Gibbon.The six volumes cover, from 98 to 1590, the peak of the Roman Empire, the history of early Christianity and its emergence as the Roman state religion, the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, the .The Fall of the Roman Empire. T he fall of the Roman Empire is usually considered the starting point for the Middle Ages.In ancient times, Rome—a term that stood not only for the city of Rome, but for the entire world dominated by the Romans—was one of .
Rome and Romans . Fall of Rome Books: Recommended reading for a modern perspective on the reasons for the fall of Rome.; End of the Republic: Content related to the men and events from the Gracchi and Marius through the turbulent years between Julius Caesar's assassination and the start of the principate under Augustus.; Why Rome Fell: 476 CE, the . The fall of the Western Roman Empire was a gradual process that took place over several decades, but the Sack of Rome in 410 AD was a key turning point in this process. The event exposed the weaknesses of the Western Empire and its emperors, and it set in motion a series of events that would ultimately lead to the Empire‘s collapse. .
Through a collection of articles, we aim to explore the many factors that contributed to the fall of Rome, including political corruption, economic instability, military defeats, and the pressures of barbarian invasions. We will also examine the aftermath of the fall of Rome, including the emergence of new powers in Europe and the lasting .The Roman Empire’s decline was not an overnight event, but rather a gradual process marked by key events that weakened its foundations. The Crisis of the Third Century, the division of the empire, and the influx of barbarian tribes each played a part in eroding Rome’s power. The date of the Fall of the Roman Empire is hard to pinpoint When Emperor Romulus was deposed in 476 AD and replaced by Odoacer, the first King of Italy, many historians believe the Empire was over. St. Valentine of Rome, patron saint of beekeepers and epilepsy, among many other things.
The Fall of the Western Roman Empire was the process of decline during which the empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided into several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control; modern historians mention factors including the effectiveness and numbers . 3. The Fall of the ‘Last Roman’: Stilicho Ivory diptych depicting Stilicho with his wif, Serena, and son Eucherius, ca. 395, now in Monza Cathedral That the political landscape of the empire was changing was confirmed by the decision in AD 395 to divide the empire between east and west. This was taken by the emperor Theodosius. The last .
why are rolex prices going down
In the fourth and final episode, Mary tackles the biggest puzzle of all: why, and how, did the Roman Empire fall? Surveying the massive walls and fortificati.
why are rolex dealers panicking
rolex stock buy or sell

You will find questions and answers regarding filing tax returns in the States .
the fall of rolex|why are rolex prices going down